In the digital age, where online connectivity drives businesses, education, and social interaction, encountering the phrase “security or firewall settings might be blocking the connection” can disrupt operations and cause significant frustration. These words often indicate that a computer or network device is being protected by security settings that, while intended to safeguard data and systems, may also inadvertently prevent legitimate connections.
This article delves into the causes, implications, and solutions for this common issue, offering a comprehensive understanding for businesses and individuals alike.
What Does the Error Mean?
At its core, the phrase “security or firewall settings might be blocking the connection” signifies that a security mechanism, such as a firewall, antivirus software, or router configuration, is preventing communication between devices or services. This often occurs when:
- A firewall rule restricts specific incoming or outgoing traffic.
- Security software detects a potential threat in a connection request.
- Network configurations are misaligned, causing legitimate traffic to be flagged.
While these measures are essential for protecting against cyberattacks, they can inadvertently block safe, necessary connections.
Common Scenarios Where This Error Occurs
1. Accessing a Website
A user may encounter this message when attempting to visit a website that is flagged as suspicious by a firewall or security software. This could be due to:
- Outdated SSL certificates on the website.
- Mismatched IP addresses or DNS errors.
- Overzealous security settings that block safe sites.
2. Using Remote Desktop Connections
Businesses reliant on remote work often face connection blocks when accessing office resources remotely. Firewalls on either the client or server side can prevent proper communication.
3. Connecting to Gaming Servers
Gamers frequently encounter this error when a game’s server communication is blocked by local or network-wide firewalls, often because the required ports are not open.
4. Email Client Issues
When configuring email clients like Outlook or Thunderbird, firewall settings might prevent them from syncing with mail servers.
5. Software and Application Updates
Security settings can block updates for essential software, particularly if the update servers are not explicitly whitelisted.
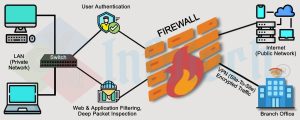
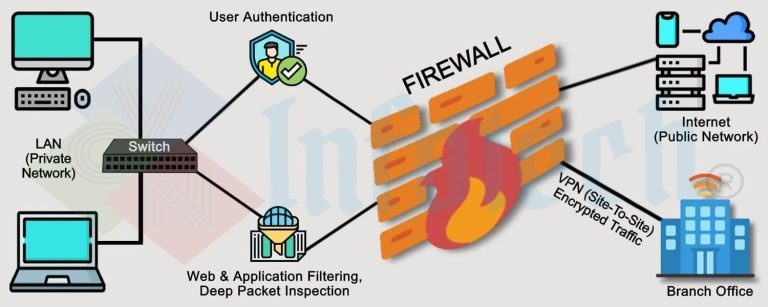
The Role of Firewalls in Connection Security
A firewall is a network security device or software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on predetermined rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external entities.
Types of Firewalls:
- Network Firewalls
Protect an entire network by filtering traffic at the router or hardware level. - Host-based Firewalls
Protect individual devices, such as computers or smartphones. - Cloud Firewalls
Designed for cloud-based resources, they secure connections to and from cloud infrastructure.
Why Firewalls Block Legitimate Connections
Although firewalls are designed to block malicious traffic, legitimate connections can also get caught in their net. This can happen due to:
- Overly Strict Security Policies: If default configurations are not adjusted to suit the specific needs of an organization or individual.
- False Positives: When legitimate traffic is misinterpreted as malicious.
- Outdated Rules: A firewall may block traffic due to outdated or irrelevant filtering rules.
- Port Restrictions: If the connection requires specific ports that are closed by default.
Troubleshooting the Issue
To resolve the issue, a systematic approach is essential. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Identify the Source of the Block
- Test the connection on a different device or network.
- Check if antivirus or other security software is active.
- Review logs in your firewall settings to identify blocked attempts.
2. Adjust Firewall Rules
- Open required ports for the application or service. For instance, remote desktop connections often require port 3389 to be open.
- Add the application or service to the firewall’s “allow” list.
- Reduce the security level temporarily to test connections (but revert it back after testing).
3. Update Security Software
Ensure that firewalls and antivirus programs are up to date. Outdated software is more likely to produce false positives.
4. Check Network Configuration
- Verify that routers or modems are not blocking the connection.
- Ensure NAT (Network Address Translation) is properly configured for remote access scenarios.
5. Test DNS Settings
Sometimes, incorrect DNS settings can trigger blocks. Switching to a public DNS, such as Google DNS (8.8.8.8), can help resolve this.
6. Consult Your IT Team
If you’re in a corporate environment, your IT team can analyze deeper configurations, including network-level firewalls and security appliances.
Preventing Future Blocks
Once the immediate issue is resolved, consider implementing preventative measures to avoid similar issues in the future.
1. Conduct Regular Audits
Regularly review firewall and security settings to ensure they align with current needs.
2. Use Application Whitelisting
Instead of blocking everything by default, allow connections for trusted applications and services.
3. Educate Users
Train users to recognize security blocks and report issues promptly. Awareness can reduce downtime caused by misconfigurations.
4. Invest in Advanced Security Solutions
Modern security solutions can intelligently differentiate between malicious and legitimate traffic, reducing the chances of false positives.
5. Maintain a Backup Connection
Have an alternate network connection ready for critical situations where immediate access is necessary.
When Security Becomes an Obstacle
While firewalls and other security tools are essential for protecting systems and data, they can also hinder productivity if improperly configured. The key lies in balancing protection and accessibility. By understanding the causes of the “security or firewall settings might be blocking the connection” error and adopting proactive measures, both individuals and organizations can maintain a secure yet functional digital environment.
In a world where connectivity is paramount, overcoming such barriers is not just a technical necessity but also a cornerstone of efficiency and innovation.